What is a variable?
Different definitions given below:
--Variable is a name of memory location
--A memory location to store temporary data within a java program.
--A variable is a container which holds the value while the java program is executed. A variable is assigned with a datatype.
--It is a combination of "vary + able" that means its value can be changed.
Different definitions given below:
--Variable is a name of memory location
--A memory location to store temporary data within a java program.
--A variable is a container which holds the value while the java program is executed. A variable is assigned with a datatype.
--It is a combination of "vary + able" that means its value can be changed.
 |
| Variable Example |
Types of Variables
1. Local variable -- used inside a method
Note: Local Variable contains garbage value
2. Instance/global variable -- used inside a class but outside method
Note: Global variable contain null or default value
3. Static variable -- We will discuss in separate post.
What is a Datatype?
--Data types specify the different sizes and values that can be stored in the variable.
--A data type is a classification of the type of data that a variable or object can hold.
There are two types of data types in Java:
1. Primitive data types: The primitive data types include Boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float and double.
2. Non-primitive data types: The non-primitive data types include String, Arrays, Classes and Interfaces.
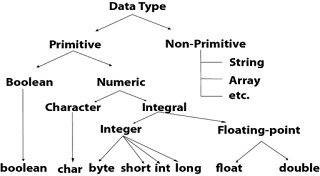 |
Data Type Hierarchy |
Classification of Data Types
 |
Classification of Data Types |
Why Java uses Unicode system?
Unicode is a universal international standard character encoding that is capable of representing most of the world's written languages. Before Unicode, there were many language standards:
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) for the United States.
ISO 8859-1 for Western European Language.
KOI-8 for Russian.
GB18030 and BIG-5 for chinese, and so on.
So to support multinational application codes, some character was using single byte, some two. An even same code may represent a different character in one language and may represent other characters in another language.
To overcome above shortcoming, the unicode system was developed where each character is represented by 2 bytes.
To get more details please watch below youtube video and Subscribe the channel.

This is great
ReplyDelete